|
| Gold V.1.3.1 signal Telegram Channel (English) |

Trump’s Tariffs Could Spark a 2025 Recession, Experts Warn
2025-03-06 @ 13:02
Is a Trump-Triggered Recession on the Horizon for 2025?
Tariffs and Trade Wars: A Looming Threat
The U.S. economy faces potential turbulence in 2025, with new tariffs and escalating trade tensions being major concerns. The Trump administration’s decision to impose additional tariffs on key trade partners—including China, Canada, and Mexico—has ignited fears of a widespread economic slowdown.
According to Jeffrey Solomon, president of TD Cowen, these tariffs could create a ripple effect across supply chains, discouraging business investments and potentially tipping the economy into recession by late 2025.
Meanwhile, affected nations are already responding:
These countermeasures could significantly slow economic growth and exacerbate inflationary pressures.
Economic Slowdown Signals Are Flashing
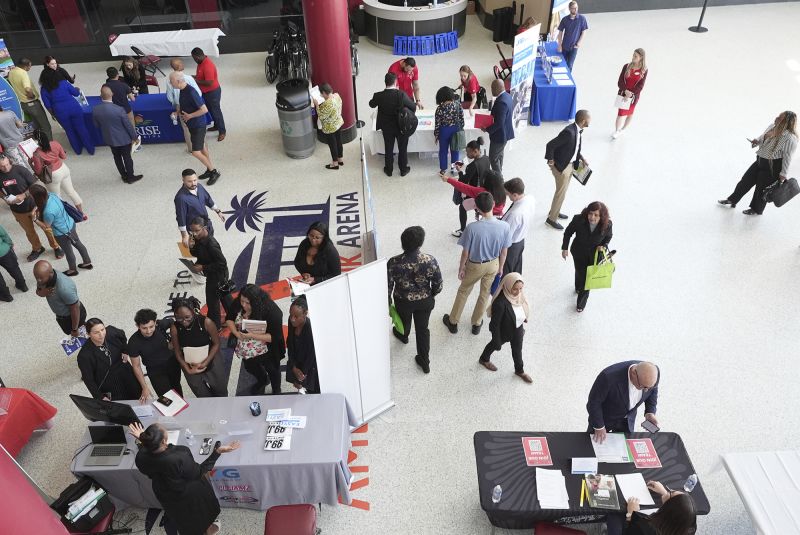
Signs of a U.S. economic slowdown are becoming increasingly apparent. Recent data from the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow model suggests the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) could shrink by 2.8% in Q1 2025, marking the first economic contraction since 2022.
Additionally, job creation is lagging, with fewer payroll additions than expected, raising concerns about labor market resilience. If hiring continues to decline, consumer spending—a key driver of the U.S. economy—could weaken further.
What Experts Are Saying
Opinions among economists and market analysts remain divided regarding the likelihood of a 2025 recession.
Optimistic Outlooks
Pessimistic Warnings
Given the mixed perspectives, the direction of the economy will largely depend on how trade policies and interest rates evolve in the coming months.
Global Economic Factors Influencing the U.S.
The global economic outlook for 2025 presents additional risks. According to Expana experts, a worldwide recession could begin by spring 2025. Key indicators include:
Tom Bundgaard, VP of Forecasting at Expana, warns that their economic models indicate a potential prolonged and deep recession. With international trade dependencies, a global slowdown could further weaken U.S. economic prospects.
Policies & Productivity: The Two Biggest Wildcards
U.S. economic performance in 2025 will also depend on domestic policy changes and productivity growth. The Atlantic Council forecasts U.S. GDP growth ranging between 1.5% and 2.7%, largely influenced by key policy shifts such as:
Additionally, labor productivity improvements, estimated to range from 1.5% to 3%, could help drive economic expansion. However, if productivity remains stagnant, it may fail to offset mounting policy risks.





![[Daily Closing 🔔] Gold – Gold Prices Surge on May 6, 2025 Amid Rising Market Uncertainty and Central Bank Buying](https://int.1uptick.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/2025-05-07T025824.761Z-file-1024x576.png)